Stroke
Types of Stroke
The effects of your stroke depend on the type of stroke, the part of the brain that was damaged and the amount of damage.
Ischemic stroke
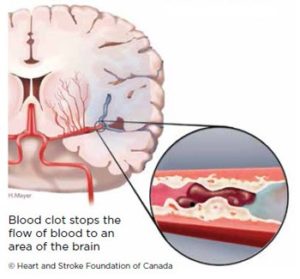 Most strokes are caused by a blockage or clot in a blood vessel in your brain. This is called ischemic stroke.
Most strokes are caused by a blockage or clot in a blood vessel in your brain. This is called ischemic stroke.
The blockage can be caused when a substance called plaque builds up on the inside wall of an artery. The blockage or clot grows as blood cells and fat cells stick to the plaque. Gradually, it grows big enough to block normal blood flow.
The blockage or clot can form in an artery in your brain. Or, it can form in an artery in another part of your body and travel to the brain.
Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
A transient ischemic attack (TIA) is caused by a small clot that briefly blocks an artery. It is sometimes called a mini-stroke or warning stroke. TIA symptoms might last only a few minutes or hours. No lasting damage occurs, but TIAs are an important warning that a more serious stroke may occur soon. They are a medical emergency — call 9-1-1.
Hemorrhagic stroke
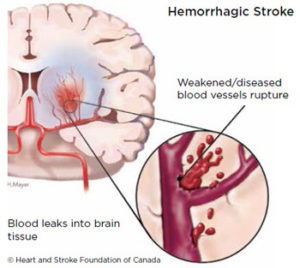 Hemorrhagic stroke is caused when an artery in the brain breaks open. The interrupted blood flow causes damage to your brain.
Hemorrhagic stroke is caused when an artery in the brain breaks open. The interrupted blood flow causes damage to your brain.
High blood pressure makes arteries weak over time. It is a major cause of hemorrhagic stroke. Weak spots in the arteries called aneurysms can stretch too far and eventually burst.
Other causes
In rare cases, a tumour, an infection, or brain swelling due to an injury or illness can cause a stroke. Some people have irregularities in their arteries at birth that can cause a stroke later in life.
How can a stroke affect my body?
The effects of stroke are different for each person. They can be mild, moderate or severe. The severity depends on factors such as:
- the type of stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic)
- the side of the brain where the stroke occurred (right or left hemisphere)
- the lobes of the brain affected by the stroke
- the size of the damaged area in the brain
- the body functions controlled by the affected area
- the amount of time the brain area had no blood flow
- the time it took to get to hospital.
Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada
One life is taken every seven minutes
For more than 60 years, Heart & Stroke has been dedicated to fighting heart disease and stroke. Our work has saved thousands of lives and improved the lives of millions of others. You’ll probably run into someone today who is alive and well thanks to the countless Canadians who have supported our cause with their time and donations.
It could be the young boy you pass on the street whose heart defect was successfully mended thanks to life-saving research. Or the woman at the coffee shop whose stroke was treated with a clot-busting drug. Or the father whose hockey teammates saved his life with CPR.
A Stroke happens when blood stops flowing to any part of your brain, damaging brain cells. The effects of a stroke depend on the part of the brain that was damaged and the amount of damage done.
- Prevention is key.
Learn more about how to live a healthier lifestyle. You’ll find help here.
heartandstroke.ca/get-healthy
- Join us to make a difference.
Get outside, have some fun and help us make heart disease and stroke a thing of the past.
heartandstroke.ca/get-involved

